Vinay Nangia, Ravi Daberao
A CASE PRESENTATION:
A male, 65 years of age, came for a second opinion of glaucoma. There was no presenting complaint. His best corrected visual acuity was 6/6 in both eyes. Anterior segment examination showed early cataractous changes in both eyes. Intraocular pressure was 20 mm Hg on Travoprost (0.004%) and brimonidine tartrate (0.2%) in both eyes. Gonioscopy showed open angles in all quadrants in both eyes. His axial length in the right eye was 24.48 mm and 24.35 mm in the left eye.

Figure 1B: Colour photograph of fundus with magnified view of the disc. Arrows are marked similar as in Fig 1A.


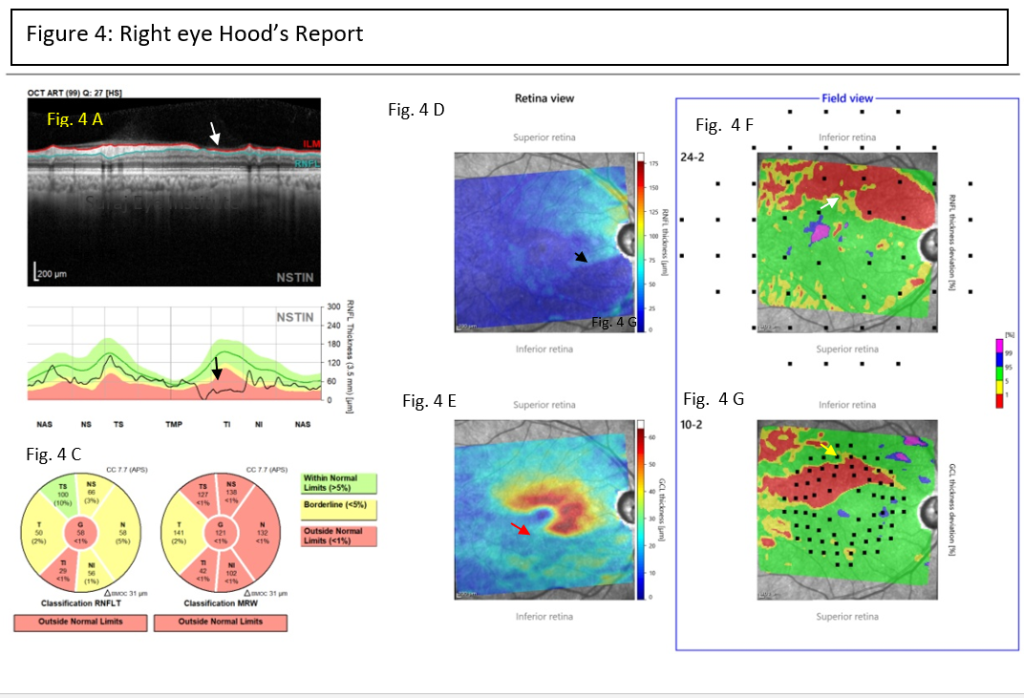
Impression: The intraocular pressure in right eye was borderline with two anti-glaucoma medications. Fundus showed cup disc ratio of 0.90, with classical wedge shaped defect of RNFL inferiorly. On OCT, patient has significant retinal nerve fiber layer and ganglion cell layer thinning in right eye. In view of the significant glaucomatous damage and for better control of intraocular pressure, patient was advised right eye trabeculectomy with mitomycin-C. It is also important to note the axial length, which was 24.48 mm and 24.35 mm in the left eye, which is considered to be on the higher side and therefore the patient was considered to be myopic. This is important because the risk of developing primary open angle glaucoma tends to increase with increasing axial length. Therefore patients that have increased axial length should be assessed carefully and all subjects who are glaucoma suspects or have glaucoma should ideally have their axial lengths measured.
Correspondence
Dr. Vinay Nangia
MS, FRCS, FRCOphth
Director
Suraj Eye Institute
Email – education@surajeye.org
